Understanding Life Skills – A Teacher’s prospective
Life skills have been defined as “the abilities for adaptive and positive behavior that enable individuals to deal effectively with the demands and challenges of everyday life” (WHO). ‘Adaptive’ means that a person is flexible in approach and is able to adjust in different circumstances. ‘Positive behavior’ implies that a person is forward looking and even in difficult situations, can find a ray of hope and opportunities to find solutions. The terms ‘Livelihood skills’ or occupational/vocational skills refer to capabilities, resources and opportunities to pursue individual and household economic goals and relate to income generation. Thus, Life skills are distinct from livelihood skills.
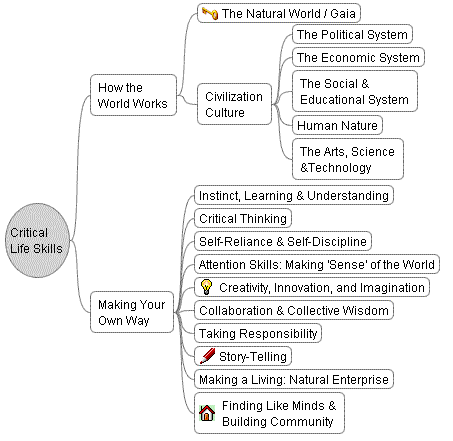
Key Life Skills
Life skills include psychosocial competencies and interpersonal skills that help people make informed decisions, solve problems, think critically and creatively, communicate effectively, build healthy relationships, empathize with others, and cope with managing their lives in a healthy and productive manner. Essentially, there are two kinds of skills - those related to thinking termed as "thinking skills"; and skills related to dealing with others termed as "social skills". While thinking skills relate to reflection at a personal level, social skills include interpersonal skills and do not necessarily depend on logical thinking. It is the combination of these two types of skills that are needed for achieving assertive behavior and negotiating effectively. “Emotional” can be perceived as a skill not only in making rational decisions but also in being able to make others agree to one's point of view. To do that, coming to terms first with oneself is important. Thus, self management is an important skill including managing/coping with feelings, emotions, stress and resisting peer and family pressure. Young people as advocates need both thinking and social skills for consensus building and advocacy on issues of concern.
The Ten core Life Skills as laid down by W.H.O are:
1. Self-awareness 2. Empathy 3. Critical thinking 4. Creative thinking 5. Decision making 6. Problem Solving 7. Effective communication 8. Interpersonal relationship 9. Coping with stress 10. Coping with emotion